Aztec
Aztec Code is one of the types of QR codes. Aztec is the name of the tribe of Indians from Central America. If you look carefully at the code, in its center you can notice a square, which looks like the Aztec pyramid, if you look at it from above. This is a special target from which you can determine the center of the code and its orientation.

Aztec Code and combines the best ideas of 2D barcodes: MaxiCode, SuperCode, CodeOne, DataMatrix, DotCode and PDF417. Despite the patent, this development has become public domain. The coding standard is described in ISO/IEC 24778:2008.
The size of the code depends on the amount of information being encoded. For example, a minimum size of 15x15 pixels allows you to encode 6 bytes, that is, 12 letters or 13 digits. The maximum size of 151x151 pixels allows encoding 1914 bytes, 3067 letters or 3832 digits.
Note that the code has two display formats: Compact, where the symbol with the target consists of two squares, and Full-Range, where the symbol with the target consists of three squares. The choice of format depends on the amount of data encoded.
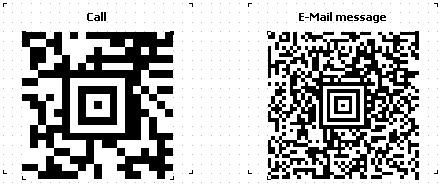
The advantage of this type of encoding over others is the ability to read the code in any orientation. Even the mirrored code will be easily read, due to the use of navigation markers.
Using a target in the center of the code allows you to read information even from distorted or stretched images.
Thanks to the Reed-Solomon encoding algorithm, the Aztec Code can be read even with partial damage. In this case, redundancy is specifically embedded in the code. The user is given the opportunity to adjust the percentage of redundant code from 5 to 95, which provides a high degree of resistance to reading errors.
The layer-by-layer structure of the code makes it possible to increase the volume of stored information by increasing the coding area.
All these advantages made Aztec Code very attractive for use in transport networks as electronic tickets, for example, in air and rail transportation. In some countries, it is used in government documentation. Like other high-density codes, Aztec codes are popular in commerce, logistics, manufacturing and pharmaceuticals.
In comparison with a QR code, Aztec Code has a higher density of recording and doesn't require fields around the code. Also, the minimum size of Aztec Code is 15x15 compared to 21x21 at QR.
To generate an Aztec Code in FastReport .NET, select the Barcode object ![]() at the Components Panel in the Report Designer. In the drop-down list, navigate to the "Two-dimensional" category, and then choose Aztec:
at the Components Panel in the Report Designer. In the drop-down list, navigate to the "Two-dimensional" category, and then choose Aztec:
After selecting the barcode, place it on the Report Page.
Double-click on the added barcode to open the editor. You can also open the barcode editor by clicking the button  in the context menu of the added object, accessed by right-clicking.
in the context menu of the added object, accessed by right-clicking.
In the barcode editor, you can choose a template for encoding information. All templates except the Swiss QR template can be used in Aztec Code. For example, a website address:
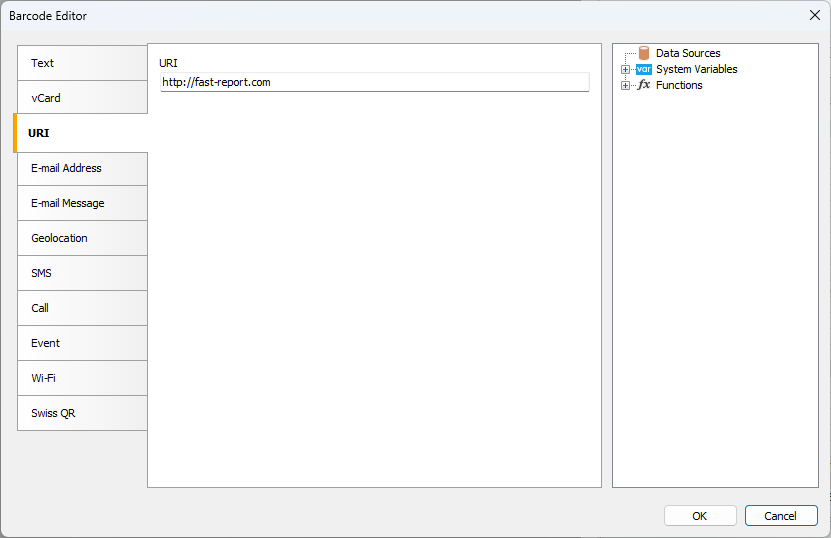
In the end the code will look like this:
